Postest Bedah Saraf
- Post Test iPass berisi soal pilihan ganda dengan waktu ujian 60 menit.
- Peserta diharapkan mengerjakan try out dengan sungguh – sungguh sebagai simulasi ujian PPDS.
- Try out hanya dapat dilakukan 1 kali untuk satu akun peserta.
- Nilai post test dan jawaban benar akan ditampilkan di akhir sesi post test
- Semua soal wajib dijawab untuk dapat mengakhiri post test
Tryout Summary
0 of 50 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the tryout before. Hence you can not start it again.
Tryout is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the tryout.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 50 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 50
1. Question
What Brodmann area corresponds to primary visual cortex?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 2 of 50
2. Question
Number 1 in this image represents what structure?
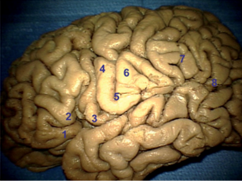 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 3 of 50
3. Question
Regions of the brain devoid of a blood-brain barrier include all of the following, EXCEPT?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 4 of 50
4. Question
A 27-year-old man is involved in a motor vehicle collision. The patient is brought to the emergency room and stabilized. Imaging demonstrates a lower cervical spinal cord injury. On exam, the patient is hypotensive and lethargic with minimal movements of the upper extremities. You suspect spinal shock and initiate pressor support. Spinal shock occurs when there are injuries to the spinal cord above level …… and the hypotension observed is due to interruption on ……. Element of the nervous system.
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 5 of 50
5. Question
The term lentiform nuclei refers to what structure(s)?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 6 of 50
6. Question
Which of the following constellations about hypothalamic function is/are correct?
- Lateral and posterior hypothalamic regions concerned with sympathetic responses
- Anterior and medial hypothalamic regions control parasympathetic responses
- Localized, bilateral lesions of the ventromedial nucleus in the tuberal region can produce hyperphagia
- Bilateral posterior hypothalamic lesions can produce poikilothermia
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 7 of 50
7. Question
The dura mater forms from what embryologic layer?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 8 of 50
8. Question
At what day of human embryogenesis does the primary neurulation begin?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 9 of 50
9. Question
A 62-year-old female undergoes microvascular decompression for hemifacial spasm. Postoperatively, she has complete ipsilateral deafness but no other neurologic deficits. The most likely cause of this deficit was in jury to one of the blood vessels that originated from which artery?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 10 of 50
10. Question
A 42-vear-old female was recently diagnosed with spontaneous intracranial hypotension. All of the following are frequently associated with this problem EXCEPT?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 11 of 50
11. Question
Refer to figure below. This disorder is caused by…
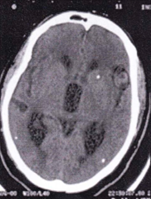 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 12 of 50
12. Question
The hand abnormality shown in figure below can be caused by injury of…
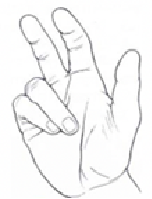 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 13 of 50
13. Question
Papez’s circuit includes all of the following structures, EXCEPT?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 14 of 50
14. Question
The afferents from the mammillothalamic tract project from the mammillary bodies to what thalamic nuclei?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 15 of 50
15. Question
What tumor is least likely to metastasize to the brain?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 16 of 50
16. Question
What neoplasm is depicted on the following contrasted T1-weighted MRI in an asymptomatic adult male?
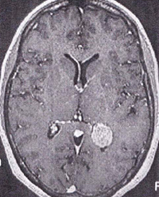 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 17 of 50
17. Question
What neoplasm is depicted on this external carotid angiogram (midarterial phase)?
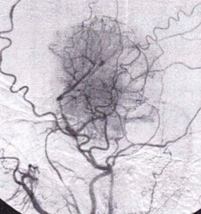 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 18 of 50
18. Question
What primary CNS neoplasm is associated with eosinophilic granular bodies?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 19 of 50
19. Question
Most common protein/stain used in Meningioma is…
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 20 of 50
20. Question
What structure is indicated by the arrow in this image from an endoscopic third ventriculostomy?
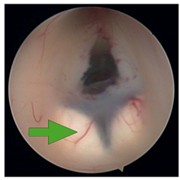 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 21 of 50
21. Question
What is the most common pineal region tumor in children?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 22 of 50
22. Question
What cranial nerves most commonly are affected in a symptomatic Chiari type 2 malformation?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 23 of 50
23. Question
What supplement during the first trimester of pregnancy is considered preventive for myelomeningocele?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 24 of 50
24. Question
What intracranial tumor is associated with polycythemia?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 25 of 50
25. Question
An 1 1-month-old boy presents with macrocrania and failure to thrive. An MRI of the brain, shown in this image, confirms what likely type of hydrocephalus?
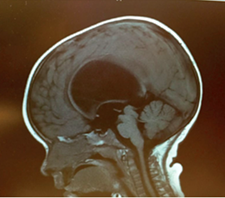 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 26 of 50
26. Question
The spinocerebellar tract (SCT) conveys proprioceptive information from the body to the cerebellum. Which pathway is correct?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 27 of 50
27. Question
A patient has a cerebellar lesion causing symptoms including impairment in the ability of standing upright and maintaining gaze direction. What is the likely location of such a lesion?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 28 of 50
28. Question
What nerve(s) provide(s) parasympathetic innervation to the kidneys?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 29 of 50
29. Question
Degenerative spondylolisthesis is most common at what level in the lumbar spine?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 30 of 50
30. Question
A 35-vear-old construction worker fell from a three-story building while at work and suffered a complete spinal cord injury at the C2 level. Which of the following functions may be preserved after a complete spinal cord injury at this level?
- Micturition
- Ejaculation
- Peristalsis
- Breathing
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 31 of 50
31. Question
Paralysis of pelvic floor muscles, symmetric saddle anesthesia, impaired erection and ejaculation, constipation, and an autonomous neurogenic bladder best describe what spinal cord lesion?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 32 of 50
32. Question
What feature of a burst fracture may imply instability and the need for surgery?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 33 of 50
33. Question
A patient with L4/L5 degenerative spondylolisthesis presents with radiculopathy. The L4 vertebral body is approximately 60% anterolisthesed. What grade is this spondylolisthesis according to the Meyerding grading scale?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 34 of 50
34. Question
Pain and temperature fibers from the face are relayed to what nucleus?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 35 of 50
35. Question
What extraocular muscle is innervated by a contralateral nucleus?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 36 of 50
36. Question
Which nucleus is the center of control for the direct and consensual pupillary light reflex?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 37 of 50
37. Question
You are falling asleep during neurosurgery teaching rounds and your co-resident pinches the back of your left arm. You immediately wake up and turn your head to the left to see what caused the Which spinal cord tract is involved, causing you to turn and look at the source of the pain?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 38 of 50
38. Question
You are evaluating a patient in the emergency department who is comatose from a large subdural He demonstrates decerebrate posturing and fixed, nonreactive pupils. What spinal cord tract mediates his peripheral response?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 39 of 50
39. Question
Which muscle is not innervated by the recurrent branch of the laryngeal nerve?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 40 of 50
40. Question
Which of the following are possible complications of mannitol administration?
- Aggravation of vasogenic edema
- Development of a hyperosmolar nonketotic state
- Acute tubular necrosis
- Hypotension
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 41 of 50
41. Question
A 42-year-old male falls 25 feet while at work and arrives at the emergency department with a Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score of 5, a dilated and nonreactive right pupil, and a mean arterial blood pressure of 80. After airway management and fluid resuscitation, his GCS improves to 7, but his right hemiparesis and nonreactive pupil remain unchanged. The patient also sustained a pelvic fracture, a left humeral fracture, splenic and liver lacerations, and multiple fractures of the cervical spine. Initial management of this patient should include:
- Begin hyperventilation to decrease the pCO2,
- Administer mannitol on arrival to the emergency department because of clinical evidence of an asymmetric exam
- Complete the primary survey, obtain cervical spine films and chest x-ray, and then move directly to CT scan
- The patient should be started on pentobarbital for elevated intracranial pressure immediately after completion of the primary survey if no mass lesion is found on CT
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 42 of 50
42. Question
In the event of trauma, what finding on a skull radiograph best indicates the possible need for emergent surgical intervention?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 43 of 50
43. Question
The presence of a “swirl” sign is described on a CT of the head. This finding indicates:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 44 of 50
44. Question
A tear in the middle meningeal artery is most likely responsible for a hemorrhage in what space/location?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 45 of 50
45. Question
You are evaluating an 82-year-old man who takes 325 mg of aspirin daily for coronary artery disease. He presented to the emergency department with a headache and sleepiness. Refer to CT shown. How long has this bleed likely been present?
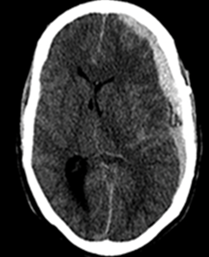 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
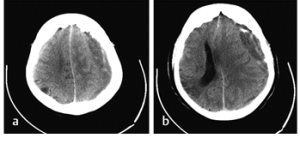
Question 46 of 50
46. Question
You are evaluating an 82-year-old man with a history of a mechanical aortic valve. He presented to the emergency department with a headache and sleepiness. What procedure would you recommend?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
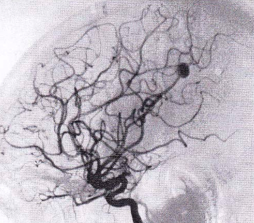
Question 47 of 50
47. Question
What is the most likely etiology of the lesion demonstrated in the following lateral internal carotid angiogram (midarterial phase)?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
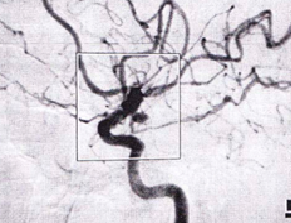
Question 48 of 50
48. Question
A 51-year-old female was taken to an emergency room after collapsing at work. She was alert and communicative, with a severe headache, photophobia, nuchal rigidity, and blurry vision. Computed tomographv (CT) of the brain revealed diffuse subarachnoid blood in the basal cisterns, mild hydrocephalus, and no intraparenchymal hematoma. Her angiogram is depicted below. What is the clinical Hunt and Hess grade of this patient?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 49 of 50
49. Question
What MR sequence is the most sensitive in identifying intracerebral cavernous malformations?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 50 of 50
50. Question
What is the arterial supply for the optic tract?
CorrectIncorrect
