iPass Drill Soal Interna 2025
Anda tidak dapat mengakses halaman ini karena belum diverifikasi oleh admin. Hubungi admin untuk info lebih lanjut.
Quiz Summary
0 of 198 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 198 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 198
1. Question
A 56-year-old man is hospitalized with an
infection for which intravenous antibiotics are required. Upon questioning,
it is revealed that he has a penicillin allergy. Which of the following
statements regarding the choice of antibiotics in this situation is
correct?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 2 of 198
2. Question
A 68-year-old woman has been hospitalized for
three days after an exacerbation of emphysema. Her clinical course
progresses well until the fourth hospital day, when she develops shortness
of breath, fatigue, and cough productive of yellow sputum. Her oxygen
saturation drops by 10%, and she is started on vancomycin and gentamicin via
rapid infusion. Thirty minutes after the initiation of antibiotics, the
patient develops erythema of the face and neck, itchiness, and hypotension.
The patient has no known drug allergies and has not been treated with
vancomycin prior to this hospitalization. Which of the following is the
mechanism of this reaction?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 3 of 198
3. Question
A 4-year-old child is brought to his
pediatrician by his mother and father. They left the child with a
baby-sitter for the first time 2 days ago He simply says, “mommy and daddy
could get sick and die when they are gone.” The child’s babysitter, when
questioned by phone, states that the child “won’t stop crying when his
parents leave.” When asked how he feels while his parents are away, the
child says, “it makes me feel sick when they are gone.” Which of the
following is the most appropriate next step?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 4 of 198
4. Question
A 25-year-old woman is receiving
desensitization shots for an allergy for the past 1 year. Today she
developed diffuse urticaria 5 minutes after the injection. Which of the
following is the most appropriate next step in management?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 5 of 198
5. Question
A 60-year-old postmenopausal woman presents
with fatigue, mild jaundice, and tingling in the lower extremities.
Laboratory studies show elevated serum levels of homocysteine and
methylmalonic acid, and mild thrombocytopenia. A peripheral blood smear
supports the diagnosis. In which of the following disorders would a
peripheral blood smear be similar to the one seen in this
case?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 6 of 198
6. Question
A 47-year-old HIV-positive woman is brought
in by ambulance after her husband called the paramedics claiming that his
wife was having difficulty breathing. Per her husband, she has been
experiencing a nonproductive cough with fever, chills, fatigue, and
difficulty catching her breath over the past couple weeks. Her last CD4+
cell count was 174/mm³, despite being on highly active antiretroviral
therapy with zidovudine, didanosine, and indinavir. Arterial blood gas
analyses show a partial arterial oxygen pressure of 59 mm Hg, partial
arterial carbon dioxide pressure of 29 mm Hg, and pH 7.56. Which of the
following is the best next step in management?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 7 of 198
7. Question
A 26-year-old woman presents to the clinic
with joint pain in her hands and wrists, difficulty breathing, and redness
over her cheeks and nose. She also notes that her fingertips change color
from white to blue to red when she is cold. Which of the following describes
the renal pathology commonly associated with this patient’s
condition?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 8 of 198
8. Question
A 33-year-old African-American man presents
to a rural clinic with a 2-day history of painful genital sores. The man
admits to sexual contact with multiple partners and has never been tested
for sexually transmitted diseases, including HIV. On physical examination
there are two tender sores with sharp edges and a yellowish exudate on his
penis. Tender unilateral inguinal adenopathy is also noted. Which of the
following is most likely to confi m the diagnosis?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 9 of 198
9. Question
A 72-year-old man presents to his primary
physician with complaints of fatigue, weight loss, dyspnea on exertion,
abdominal pain, and dark blood in the stool. Although the patient had a
negative sigmoidoscopy on routine examination 6 months ago, colon cancer is
strongly suspected. Which is the best diagnostic modality to use in this
patient?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 10 of 198
10. Question
A 7-year-old boy is brought to the physician
by his parents because of recurrent sinus infections. The parents state that
the boy also has had multiple lung infections and intermittent diarrheal
infections since birth. Which of the following results would most likely be
found on further testing?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 11 of 198
11. Question
A patient is administered a tuberculin test.
Which of the following types of hypersensitivity reaction is being tested,
and which cells would be expected to mediate a positive test
result?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 12 of 198
12. Question
A 3-year-old boy is brought to his
pediatrician because of worsening cough and rhinorrhea. His parents state
that he has had multiple similar episodes over the past year with two brief
hospitalizations for pneumonia. Physical examination of the skin reveals the
lesion seen in the image. Laboratory tests show very low serum levels of
IgA. Which of the following is most likely to also be seen in this
child?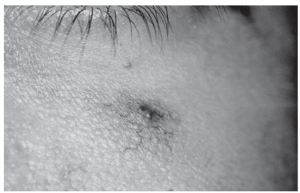 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 13 of 198
13. Question
An important clinical difference between
urticaria and angioedema isCorrectIncorrect -
Question 14 of 198
14. Question
Which of the following best describes the
patient with common variable immunodeficiency?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 15 of 198
15. Question
A 25-year-old female complains of watery
rhinorrhea and pruritus of the eyes and nose that occurs around the same
season each year. Symptoms are not exacerbated by weather changes, emotion,
or irritants. She is on no medications and is not pregnant. Which of the
following statements is correct?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 16 of 198
16. Question
A 20-year-old nursing student complains of
asthma while on her surgical rotation. She has developed dermatitis of her
hands. Symptoms are worsened when in the operating room. Which of the
following is correct?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 17 of 198
17. Question
A 30-year-old male develops skin rash,
pruritus, and mild wheezing about 20 minutes after an intravenous pyelogram,
performed for the evaluation of renal stone symptoms. The best approach to
diagnosis of this patient includes:CorrectIncorrect -
Question 18 of 198
18. Question
Appropriate acute management for patient on
number 18 would includeCorrectIncorrect -
Question 19 of 198
19. Question
Immunological mechanisms play a role in many
hematological disorders. Which of the following statements is
correct?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 20 of 198
20. Question
A 19-year-old female university student
unknowingly eats a noodle dish that has shrimp in it. She is allergic to
shrimp. Over the next 20 minutes she develops acute skin lesions consisting
of erythematous wheals that are raised on the surface of the skin. Which of
the following is most characteristic of these lesions?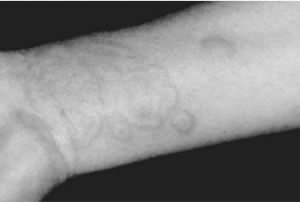 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 21 of 198
21. Question
A 43-year-old man with episodic, severe
hypertension is referred for evaluation of possible secondary causes of
hypertension. He reports feeling well generally, except for episodes of
anxiety, palpitations, and tachycardia with elevation in his blood pressure
during these episodes. Exercise often brings on these events. The patient
also has mild depression and his current medications include sertraline,
labetalol, amlodipine, and lisinopril. Urine 24-hour total metanephrines are
ordered and show an elevation of 1.5 times the upper limit of normal. Which
of the following is the next most appropriate step?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 22 of 198
22. Question
A 29-year-old woman is evaluated for anxiety,
palpitations, and diarrhea and found to have Graves disease. Before she
begins therapy for her thyroid condition, she has an episode of acute chest
pain and presents to the emergency department. Although a CT angiogram is
ordered, the radiologist calls to notify the treating physician that this is
potentially dangerous. Which of the following best explains the
radiologist’s concern?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 23 of 198
23. Question
A 37-year-old obese woman presents to clinic
for routine health evaluation. She reports that over the last year she has
had two yeast infections treated with over the counter remedies and she
frequently feels thirsty. She reports waking up at night to urinate. Which
of the following studies is the most appropriate first test in evaluating
this patient for diabetes mellitus?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 24 of 198
24. Question
Which of the following laboratory values is
typically seen in hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state and not in diabetic
ketoacidosis?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 25 of 198
25. Question
A 75-year-old man presents to his physician
with a 4-week history of exertional shortness of breath. He worked as a pipe
fitter for 45 years, retiring 5 years ago. He denies chest pain,
palpitations, swelling in his legs, cough, hemoptysis, and weight loss. He
smokes 1 pack per day and has done so for the past 45 years. Pulmonary
function testing shows a mild restrictive pattern with a normal diffusing
capacity. X-ray of the chest shows linear opacities at the lung bases and
pleural plaques. Which of the following is the most appropriate
intervention?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 26 of 198
26. Question
A 54-year-old woman is diagnosed with type 2
diabetes mellitus after a routine followup for impaired fasting glucose
showed that her hemoglobin A1c is now 7.6%. She has attempted to lose weight
and exercise with no improvement in her hemoglobin A1c, and drug therapy is
now recommended. She has mild systemic hypertension that is well controlled
and no other medical conditions. Which of the following is the most
appropriate first-line therapy?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 27 of 198
27. Question
A 21-year-old woman with a history of type 1
diabetes mellitus is brought to the emergency department with nausea,
vomiting, lethargy, and dehydration. Her mother notes that she stopped
taking insulin 1 day before presentation. She is lethargic, has dry mucous
membranes, and is obtunded. Blood pressure is 80/40, and heart rate is 112
beats/min. Serum sodium is 126 mEq/L, potassium is 4.3 mEq/L, magnesium is
1.2 mEq/L, blood urea nitrogen is 76 mg/dL, creatinine is 2.2 mg/dL,
bicarbonate is 10 mEq/L, and chloride is 88 mEq/L. Serum glucose is 720
mg/dL. All the following are appropriate management steps
EXCEPT:CorrectIncorrect -
Question 28 of 198
28. Question
Which of the following regarding care of the
hospitalized diabetic patient is true?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 29 of 198
29. Question
Which of the following patients should be
treated with either an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or
angiotensin receptor blocker?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 30 of 198
30. Question
Plasma glucose is normally tightly regulated
in the body, with fasting levels between 70 and 110 mg/dL. When the blood
glucose falls below 80–85 mg/dL, which of the following physiologic changes
is the first to occur?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 31 of 198
31. Question
A 25-year-old health care worker is seen for
evaluation of recurrent hypoglycemia. She has had several episodes at work
over the past year in which she feels shaky, anxious, and sweaty; she
measures her fingerstick glucose, and it is 40–55 mg/dL. This has been
confirmed with a plasma glucose level during one episode of 50 mg/dL. She
then drinks orange juice and feels better. Aside from oral contraceptives,
she takes no medications and is otherwise healthy. Which of the following
tests is most likely to demonstrate the underlying cause of her
hypoglycemia?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 32 of 198
32. Question
A 35-year-old woman is evaluated for new
headaches with a brain MRI. A pituitary lesion is visualized. Which of the
following laboratory findings would be suggestive of a functional pituitary
adenoma?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 33 of 198
33. Question
Which of the following statements regarding
the epidemiology of metabolic syndrome is true?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 34 of 198
34. Question
A 68-year-old African-American man presents
to his primary care physician for a check-up. He has not been to the
physician’s office in over 15 years. He reports that he is fine but that his
wife keeps telling him that he has to “go see the doctor.” His wife is in
the room and says that he recently has had some problems swallowing food and
that he is losing weight The physician is concerned and orders an endoscopy,
which reveals a biopsy positive for squamous cell carcinoma of the
esophagus. Which of the following most likely could have prevented this
condition?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 35 of 198
35. Question
A 30-year-old man is admitted to the hospital
for active pulmonary tuberculosis with a positive sputum acidfast bacilli
smear. He is HIV positive with a CD4 count of 45/μL and is not on highly
active antiretroviral therapy. Which of the following is the most
appropriate initial therapy?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 36 of 198
36. Question
A 67-year-old man is evaluated by the
emergency department for blood in the toilet bowl after moving his bowels.
Blood was also present on the toilet paper after wiping. He does report
straining and recent constipation. He has a history of systemic hypertension
and hyperlipidemia. Vital signs are normal, and he is not orthostatic.
Anoscopy shows external hemorrhoids, hematocrit is normal, and bleeding does
not recur during his 6-hour emergency department stay. Which of the
following is the most appropriate management?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 37 of 198
37. Question
A 67-year-old man is evaluated by the
emergency department for blood in the toilet bowl after moving his bowels.
Blood was also present on the toilet paper after wiping. He does report
straining and recent constipation. He has a history of systemic hypertension
and hyperlipidemia. Vital signs are normal, and he is not orthostatic.
Anoscopy shows external hemorrhoids, hematocrit is normal, and bleeding does
not recur during his 6-hour emergency department stay. Which of the
following is the most appropriate management?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 38 of 198
38. Question
A 21-year-old woman presents to the emergency
department complaining of diarrhea, heart palpitations, anxiety, and diffuse
abdominal pain. Vital signs show tachycardia. The patient wanted to lose
weight and started taking her mother’s medication to do so; she does not
know for which condition the medication was prescribed. Her friend had
similar symptoms not long ago and was treated for her condition. Which of
the following most likely accounts for this patient’s
presentation?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 39 of 198
39. Question
A 45-year-old woman presents to her doctor
with feelings of fatigue, increased appetite, increased sweating, and
palpitations. Her doctor also notes that her eyes appear unusual. She
receives pharmacologic treatment for her condition, but soon develops a
fever and multiple infections in her throat and gastrointestinal tract. Her
doctor quickly discontinues the medication. Which medication was she most
likely prescribed?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 40 of 198
40. Question
A 66-year-old man with a 50-pack-year history
of cigarette smoking comes to the clinic complaining of chronic cough,
dyspnea, and blood in his sputum. He says he has been feeling lethargic and
has lost 18 kg (40 lb) over the past three months with no changes in diet or
exercise. While awaiting x-ray of the chest, the patient suffers a seizure
and is rushed to the emergency department of the nearest hospital.
Laboratory studies show a serum sodium level of 120 mEq/dL. Which of the
following is most likely to be elevated in this patient?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 41 of 198
41. Question
A 44-year-old woman presents to her physician
with a one month history of fatigue, polyuria, and polydipsia. Laboratory
studies show a glucose level of 350 mg/dL. The physician decides to
prescribe a medication to treat diabetes mellitus. He warns the patient that
an adverse effect of the medication is lactic acidosis. Which of the
following is the most likely mechanism of action of the
medication?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 42 of 198
42. Question
A 54-year-old woman presents to the physician
with diabetes mellitus, osteoporosis, and hypertension. She has noted a
recent weight gain and abdominal striae. Laboratory studies show a decreased
ACTH level. A single mass is noted adjacent to the right kidney on abdominal
CT scan. Neither low- nor high-dose dexamethasone suppresses the patient’s
cortisol production. Which of the following is the most likely explanation
for these findings?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 43 of 198
43. Question
A 60-year-old woman with a 55-pack-year
smoking history presents to the emergency department complaining of nausea
and vomiting, headache, malaise, and diffuse bone pain. CT shows a solitary
nodule in the upper lobe of the right lung. Laboratory studies are
significant for a serum calcium level of 14.2 mg/dL, serum phosphate of 1.5
mg/dL, and serum alkaline phosphatase activity of 81 U/L. The factor that
accounts for this patient’s laboratory findings acts primarily at which of
the following locations?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 44 of 198
44. Question
A 26-year-old man presents with increased
thirst, urinary frequency, and nocturia over the past several months.
Physical examination is unremarkable. Twenty-four-hour urine osmolarity is
<300 mOsm/L. A fl uid deprivation test does not result in an increased urine osmolarity. Administration of 0.03 μg/kg of desmopressin results in a urine osmolarity of 450 mOsm/L after 2 hours. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 45 of 198
45. Question
A 45-year-old woman with chronic alcohol
abuse admitted 3 days ago for nausea and severe diarrhea now complains of
perioral and finger tingling. She was admitted for hydration after 1 week of
severe watery diarrhea. She has been receiving intravenous hydration and
dextrose but has not been able to take oral nutrition secondary to continued
nausea. Her blood pressure is 130/74 mm Hg, pulse is 68/min, and respiratory
rate is 16/min. She is afebrile. Physical examination is significant for
facial twitching on percussion of her facial nerve just anterior to the ear,
as well as the induction of carpal spasm after the inflation of a blood
pressure cuff on her arm. Which of the following is most likely to have
caused these findings?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 46 of 198
46. Question
An 18-year-old woman presents to the
emergency department with acute mental status changes, rapid and deep
breathing, abdominal pain, and vomiting. On examination she is tachypneic
and tachycardic, her abdomen is soft and nontender, and her mucous membranes
are dry. Laboratory values are notable for a potassium level of 5.5 mEq/L,
bicarbonate of 12 mEq/L, and serum glucose of 400 mg/dL. Which of the
following is the most appropriate strategy during the first 24
hours?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 47 of 198
47. Question
A 55-year-old white man with a 20-year
history of gastroesophageal reflux visits the clinic for worsening reflux
symptoms over the past 18 months. His last visit was 7 years ago and he
claims to be otherwise in good health. He has been compliant with his
antireflux medications, including an H2-blocker and a proton pump inhibitor.
Which of the following is the best next step in management?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 48 of 198
48. Question
A 58-year-old man comes to the emergency
department complaining of colicky abdominal pain over the past 3 days that
suddenly became more severe and constant over the past 6 hours. A contrast
study is performed and results are shown in the image. What is the
first-line treatment in this patient?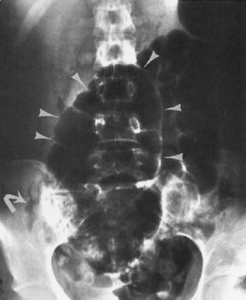 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 49 of 198
49. Question
Which of the following statements regarding
gastrointestinal symptoms is TRUE?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 50 of 198
50. Question
A 45-year-old HIV-positive woman comes to her
primary care physician complaining of a 2- day history of bloody diarrhea.
She states that she has been feeling well until 2 days ago, when she
developed abdominal pain. She denies fevers, chills, night sweats, nausea,
or vomiting. She admits to feeling tired over the last couple of weeks and
has had a 2.3-kg (5- lb) weight loss over the past 2 weeks. Her stool sample
shows WBCs and RBCs. Her Gram stain is shown in the image. Her CD4+ cell
count is 201/mm³. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this
woman’s symptoms?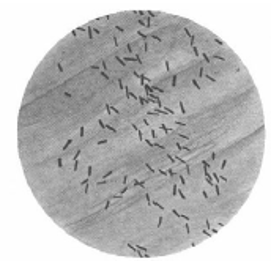 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 51 of 198
51. Question
A 24-year-old woman presents to her primary
care provider because of bloody diarrhea for several months and uveitis.
Complete blood cell count shows mild anemia but a normal WBC count. The
erythrocyte sedimentation rate and the C-reactive protein level are not
elevated. Which of the following is the most likely
diagnosis?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 52 of 198
52. Question
A 57-year-old female wishes to undergo a
screening colonoscopy for colon cancer. She has no family history of colon
cancer and currently has no symptoms referable to the gastrointestinal
tract. Which of the following statements is true about colonoscopy as a
screening test for colon cancer?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 53 of 198
53. Question
Which of the following statements regarding
therapy for gastroesophageal reflux (GERD) therapy is TRUE?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 54 of 198
54. Question
A 44-year-old woman complains of 6 months of
epigastric pain that is worst between meals. Her stools are heme positive.
She undergoes esophagogastroduodenoscopy, which demonstrates a
well-circumscribed, 2-cm duodenal ulcer that is positive for Helicobacter
pylori. Which of the following is the recommended initial therapy given
these findings?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 55 of 198
55. Question
A 36-year-old male has had Crohn disease for
5 years. His disease was initially managed with occasional tapers of oral
prednisone, followed by use of oral budesonide. Over the last 6 months he
has required two courses of oral prednisone and was hospitalized for
worsening abdominal pain and fevers requiring IV antibiotics and
corticosteroids. He has not had evidence of fistulizing disease. How should
his Crohn disease be managed at this time?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 56 of 198
56. Question
A 78-year-old woman is admitted to the
hospital with fever, loss of appetite, and left lower quadrant pain. She is
not constipated but has not moved her bowels recently. Laboratory
examination is notable for an elevated white blood cell count. These
symptoms began approximately 3 days ago and have steadily worsened. Which of
the following statements regarding her likely condition is
true?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 57 of 198
57. Question
A 48-year-old man is diagnosed with carcinoid
syndrome after presenting with diarrhea, flushing, and hypotension. He
remains fatigued with a loss of appetite and irritability. On examination,
you notice his tongue is bright red and somewhat enlarged. It is tender to
touch. In addition, he has a pigmented and scaling rash that is most
prominent around his neckline. Which of the following is the most likely
vitamin or mineral deficiency in this patient?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 58 of 198
58. Question
A 51-year-old alcoholic man presents to the
emergency department complaining of vomiting blood. On further evaluation
including gastric lavage, you determine that he is not experiencing an upper
gastrointestinal bleed, but he is having significant gingival bleeding. He
is intoxicated and complains of fatigue. Reviewing his chart, you find that
he had a hemarthrosis evacuated 6 months ago and has been lost to follow-up
since then. He takes no medications. Laboratory data show platelets of
250,000 and international normalized ratio of 0.9. He has a diffuse
hemorrhagic eruption on his legs that is centered around hair follicles.
Which of the following is the recommended treatment for this patient’s
underlying disorder?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 59 of 198
59. Question
A 21-year-old woman is admitted to the
cardiac care unit after collapsing in her college dormitory. When emergency
personnel arrived, she was found to be in a torsades de pointes arrhythmia
and was pulseless. She received cardiopulmonary resuscitation,
defibrillation, and magnesium en route to the hospital. On arrival, her
initial potassium is 1.2 mEq/L. Her physical examination is remarkable for
an excessively thin appearance with lanugo hair on arms and chest. Her body
mass index is 14.6 kg/m2. Which of the following statements is true
regarding this patient’s nutritional state?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 60 of 198
60. Question
A 23-year-old woman presents to the clinic
complaining of symptoms of weight loss and chronic diarrhea. She has no past
health issues and is not taking any medications. On physical examination,
she appears unwell and cachectic. Routine laboratory tests reveal a low
hemoglobin level and an increased international normalized ratio (INR) even
though she is not taking any anticoagulants. The liver enzymes are normal,
but the albumin and calcium levels are low, suggesting generalized
malnutrition. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial
diagnostic test for malabsorption?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 61 of 198
61. Question
A 29-year-old woman presents to the clinic
complaining of symptoms of dysphagia with solids and liquids. The symptoms
are worse when she is eating quickly or is anxious. Her physical examination
is normal. Esophageal manometry reveals normal basal esophageal sphincter
pressure, with no relaxation of the sphincter on swallowing. Which of the
following is the most appropriate next step in management?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 62 of 198
62. Question
A 40-year-old taxicab driver presents to the
clinic for evaluation of worsening abdominal pain. The symptoms seem to get
worse after meals and the pain is described as a dull burning sensation with
no radiation. Antacids previously alleviated the pain but do not seem to be
effective now and his only medication is prn use of naproxen for lower back
pain. On physical examination, there is epigastric tenderness but no
rigidity or masses. Diagnostic upper endoscopy is performed with the
findings seen in Figure 4–4. Which of the following is the most likely
diagnosis?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 63 of 198
63. Question
A 43-year-old man presents to the clinic for
evaluation of feeling unwell. His symptoms are vague and nonspecific.
Physical examination is unremarkable except for evidence of scleral icterus,
but no hepatomegaly or ascites. The skin appears normal. Which of the
following is the most likely explanation for why early jaundice is visible
in the eyes but not the skin?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 64 of 198
64. Question
A 57-year old man comes to the office with a
complaint of food “sticking on the way down.” His past medical history
includes hypertension, type 2 diabetes, and dyslipidemia. His physical
examination is completely normal. Which of the following characteristics
suggests a benign problem is causing the dysphagia?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 65 of 198
65. Question
A 27-year-old man with HIV comes to the
clinic with symptoms of pain every time he swallows (odynophagia). He is not
on any antiretroviral therapy and otherwise feels well. Examination of the
mouth and pharynx are normal. Which of the following is the most likely
diagnosis?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 66 of 198
66. Question
A 45-year-old woman presents to the emergency
department with a 1-week history of jaundice, anorexia, and right upper
quadrant discomfort. On examination she is icteric, with a tender righ upper
quadrant and liver span of 14 cm. There is no shifting dullness or pedal
edema and th heart and lungs are normal. On further inquiry, she reports
consuming 1 bottle of wine a day for the past 6 months. Which of the
following laboratory tests is most characteristic of a patient with jaundice
secondary to alcoholic hepatitis?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 67 of 198
67. Question
A 22 year-old-woman is brought to the
emergency room 2 hours after ingesting 30 tablets of acetaminophen (500
mg/tab). Her past medical history is significant for depression, but this is
the first self-harm attempt. She is admitted to the hospital for further
management of an acetaminophen overdose. Which of the following is the
mostly likely mechanism of acetaminophen hepatotoxicity?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 68 of 198
68. Question
Which of the following is the most
appropriate next step in management of acetaminophen
toxicity?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 69 of 198
69. Question
A 61-year-old woman is brought to the
emergency department drowsy and disoriented, able only to follow simple
commands. On examination her abdomen is distended and nontender, her skin
has a yellow hue, and there are multiple spider nevi on her chest. In her
purse, the physician fi nds prescriptions for peginterferon and ribavirin.
When asked to raise her hands, the physician notices a coarse tremor.
Laboratory tests show: Aspartate aminotransferase: 89 U/L Alanine
aminotransferase: 93 U/L Total bilirubin: 3.1 mg/dL Ammonia: 124 μg/dL Which
of the following is the most likely diagnosis?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 70 of 198
70. Question
Which of the following statements regarding
liver function tests is true?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 71 of 198
71. Question
Which of the following is true about
aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) in liver
injury?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 72 of 198
72. Question
A 34-year-old man presents to the physician
complaining of yellow eyes Hepatitis serologies are sent and reveal the
following: Hepatitis A IgM: negative; Hepatitis A IgG: negative; Hepatitis B
core IgM: positive; Hepatitis B core IgG: negative; Hepatitis B surface
antigen: positive; Hepatitis B surface antibody: negative; Hepatitis B e
antigen: positive; Hepatitis B e antibody: negative; Hepatitis C antibody:
positive; What is the cause of the patient’s current clinical
presentation?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 73 of 198
73. Question
A 16-year-old girl had visited your clinic 1
month ago with jaundice, vomiting, malaise, and anorexia. Two other family
members were ill with similar symptoms. Based on viral serologies, including
a positive anti-hepatitis A virus IgM, a diagnosis of hepatitis A was made.
The patient was treated conservatively, and 1 week after first presenting,
she appeared to have made a full recovery. She returns to your clinic today
complaining of the same symptoms she had 1 month ago. She is jaundiced, and
an initial panel of laboratory tests returns elevated transaminases. Which
of the following offers the best explanation of what has occurred in this
patient?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 74 of 198
74. Question
Which of the following statements is true
about the prevention of viral hepatitis?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 75 of 198
75. Question
Which of the following statements is true
about drug-induced liver injury (DILI)?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 76 of 198
76. Question
A 46-year-old man is known to have chronic
hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. He is a former IV drug user for more than
20 years who has been abstinent from drug use for 1 year. He was treated for
tricuspid valve endocarditis 3 years previously. He does not know when he
acquired HCV. His laboratory studies show a positive HCV IgG antibody with a
viral load of greater than 1 million copies. The virus is genotype 2. His
aspartate aminotransferase is 82 IU/L, and his alanine aminotransferase is
74 IU/L. He undergoes liver biopsy, which demonstrates a moderate degree of
bridging fibrosis. Which of the following is the most predictive of the
development of cirrhosis?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 77 of 198
77. Question
Which of the following statements is true
about potential treatment options for his hepatitis C virus?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 78 of 198
78. Question
A 34-year-old woman is evaluated for fatigue
malaise, arthralgias, and a weight loss over the past 6–8 weeks. Since
feeling poorly, she has taken approximately one or two tablets of
acetaminophen 500 mg daily. She has scleral icterus. Her liver edge is
palpable 3 cm below the right costal margin. It is smooth and tender. The
spleen is not enlarged. She has mild synovitis in the small joints of her
hands. Her aspartate aminotransferase is 542 IU/L, alanine aminotransferase
is 657 IU/L, alkaline phosphatase is 102 IU/L, total bilirubin is 5.3 mg/dL,
and direct bilirubin is 4.8 mg/dL. Which of the following tests would be
LEAST likely to be positive in this diagnosis?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 79 of 198
79. Question
Which of the following is true about the
pathophysiology of alcoholic liver disease?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 80 of 198
80. Question
A 55-year-old man with cirrhosis thought
secondary to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis presents with altered mental
status. All of the following can precipitate hepatic encephalopathy in this
type of patient EXCEPT:CorrectIncorrect -
Question 81 of 198
81. Question
A 30-year-old patient with a history of mild
persistent asthma (baseline peak expiratory flow rate of 85%) presents to
the emergency department with shortness of breath and wheezing that has not
relieved by her albuterol inhaler for the past 12 hours. She was able to
tolerate pulmonary function tests and a set was performed. Which of the
following is the most likely test result?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 82 of 198
82. Question
A 65-year-old smoker previously diagnosed
with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease presents to the emergency
department complaining of worsening cough and sputum production. She reports
feeling breathless when climbing the stairs to her first floor walk-up
apartment, and has moderate difficulty in providing her history in complete
sentences. X-ray of the chest shows hyperinflated lungs with flattened
diaphragms, attenuated vascular markings, and a narrow mediastinum. What
agent(s) will provide the greatest relief of symptoms in the emergency
department?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 83 of 198
83. Question
A 30-year-old man has episodes of wheezing
and shortness of breath two to three times per week. Approximately every 2
weeks he awakens at night due to cough and difficulties breathing. He
reports having similar symptoms since he was a child, but believes that they
are worsening somewhat now. His symptoms are worsened by cold air and
exercise and are improved by rest. Which of the following is the most
appropriate treatment?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 84 of 198
84. Question
A 30-year-old man presents to the
resuscitation bay with gunshot wounds in the anterior and posterior left
chest. Although in distress and dyspneic, the patient is cooperative. He has
a patent airway and is moving all extremities. His pulse is 120/min, blood
pressure is 120/90 mm Hg, and respiratory rate is 30/min. He has bounding
distal pulses, and no other injuries are identified on secondary
examination. X-ray of the chest reveals fluid in the pleural space, and a
left chest tube thoracostomy yields 600 mL of bright red fluid. Over the
next hour 750 mL of blood is collected. What is the most appropriate next
step in management?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 85 of 198
85. Question
A 5-year old girl is brought to the emergency
department in December by her mother, who complains that her daughter seems
confused. The mother reports that her daughter has complained of
intermittent headaches since the two of them moved into the first floor of
an older apartment building 6 months ago. The mother has been at home with
the daughter for the past 24 hours and the girl appears lethargic and is
complaining of joint aches, nausea, and a headache. Her pulse is 120/min,
blood pressure is 130/85 mm Hg, respiratory rate is 25/min, and oxygen
saturation is 100% on room air. The girl’s mother also notes having a slight
headache that started yesterday. Which of the following diagnostic tests
should be most rapidly pursued?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 86 of 198
86. Question
A 53-year-old man presents to the clinic with
complaints of increasing shortness of breath, a nagging cough, and weight
loss over several months. He reports no history of cigarette smoking but has
worked underground in the New York City subway system for the past 20 years.
Spirometry demonstrates an FEV1:FVC ratio of 0.7 and an FEV1 value that is
60% of expected. The FEV1 improves to 70% of expected with bronchodilator
treatment. Which of the following is the most likely
diagnosis?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 87 of 198
87. Question
A 55-year-old man presents to his physician’s
office with increasing dyspnea on exertion. He denies chest pain,
diaphoresis, nausea, or vomiting. He has been involved in eight motor
vehicle accidents in the past 3 years. Past medical history is significant
for hypertension, for which he takes a diuretic. His temperature is 37.2°C
(99.0°F), blood pressure is 121/82 mm Hg, pulse is 85/min, respiratory rate
is 14/min, and oxygen saturation is 99% on room air. Physical examination is
significant for a body mass index of 35 kg/m², a diffuse and laterally
displaced point of maximal intensity, and an S3 gallop. Which of the
following is the most appropriate next step in diagnosing his most likely
underlying condition?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 88 of 198
88. Question
A 33-year-old farmer presents to the clinic
with symptoms of recurrent wheezing and coughing after working in a barn
where hay is stored. He has no prior history of asthma, and is not taking
any medications. On physical examination, there are bibasilar crackles on
auscultation of the lungs, the heart sounds are normal, JVP is 2 cm above
the sternal angle, and there is no peripheral edema. His laboratory
investigations are normal with no increase in eosinophils on the CBC. The
chest x-ray (CXR) reveals patchy lower lobe infiltrates, and a normal
cardiac silhouette. Which of the following is the most likely
diagnosis?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 89 of 198
89. Question
A 53-year-old man presents to the hospital
with increasing symptoms of shortness of breath, increased sputum
production, and frequent puffer use. He has a prior history of chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) as a result of a 44 pack/year history
of smoking He is admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of acute
exacerbation of COPD and started on oxygen, antibiotics, oral steroids,
inhaled bronchodilators, and anticholinergic agents. The next day he is
found in his room confused and sleepy. An arterial blood gas reveals a PO2
110mm Hg, and PCO2 75 mm Hg. Which of the following explanations regarding
his elevated PCO2 is correct?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 90 of 198
90. Question
A 63-year-old man presents to the clinic for
evaluation of symptoms of shortness of breath. The symptoms are worse on
exertion, but there is no chest discomfort, cough, or sputum production. His
physical examination is completely normal. Investigations include a normal
CXR, and on the arterial blood gas the PO2 is 74 mm Hg, and PCO2 is 60 mm
Hg. Which of the following mechanisms is the most likely cause for the
elevated PCO 2?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 91 of 198
91. Question
A 56-year-old man presents to the clinic for
assessment of symptoms of chronic cough. It is present most of the time and
is progressively getting worse over the past 3 years. With the cough he
usually has white to yellow sputum that he has to expectorate. There is no
history of wheezing, asthma, heart failure (HF), or acid reflux disease. He
currently smokes 1 pack a day for the past 35 years. On examination, his
chest is clear. CXR is normal and his forced expiratory volume in 1 second
(FEV1) and forced vital capacity (FVC) on spirometry are normal. Which of
the following is the most likely diagnosis?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 92 of 198
92. Question
A 40-year-old man presents to the clinic for
assessment of fever, chills, sore throat, and cough. The symptoms started 2
days ago and his sputum is now productive and greenyellow in color. His past
medical history is negative, and he reports his son having a similar illness
1 week ago. The physical examination is normal. A CXR is performed, which
reveals a posterior mediastinal mass, but no pneumonia. Which of the
following is the most likely diagnosis?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 93 of 198
93. Question
A 44-year-old woman has been complaining of a
4-year history of increasing dyspnea and fatigue. Physical examination
reveals increased JVP and a reduced carotid pulse. Precordial examination
reveals a left parasternal lift, loud P2, and right-sided S3 and S4. There
are no audible murmurs. CXR reveals clear lung fields and an ECG shows
evidence of right ventricular hypertrophy. Pulmonary function tests show a
slight restrictive pattern. A diagnosis of primary pulmonary hypertension
(PPH) is made. Which of the following is the most likely cause of death in
this condition?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 94 of 198
94. Question
A 42-year-old woman presents to your office
again after 16 years of intermittent severe left lower quadrant abdominal
pain. She denies having weight loss, fever, or chills. The cause of her
symptoms is not apparent from previous workups, which included a complete
blood cell count, electrolyte evaluations, urinalysis, computed tomographic
scan of the abdomen and pelvis, colonoscopy, and gynecologic examination.
She has previously been thoroughly evaluated for episodic dizziness,
headaches, fl ulike syndromes, back pain, and pain with intercourse. The
results of all these workups were negative. What is the most likely
diagnosis?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 95 of 198
95. Question
A 32-year-old woman states that over the past
6 months she has felt constantly nervous. She adds that sometimes, “I feel
like my heart is going to burst.” She also notes that her heart skips a beat
from time to time, and that she is having trouble sleeping. The patient also
complains of increased bowel movements and weight loss, along with
significant weakness when she attempts to climb stairs or lift heavy items.
Her temperature is 37.8°C (100.1°F), pulse is 102/min, blood pressure is
124/85 mm Hg, and respiratory rate is 18/min. Which of the following is the
best management?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 96 of 198
96. Question
A 18-year-old single mother finds herself
being overprotective with her child. The mother would like to go back to
school and pursue her passion for writing but is unable to afford daycare.
She often finds herself regretting her pregnancy. The child is a product of
an unplanned pregnancy. Which of the following is the most likely defense
mechanism this patient is using?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 97 of 198
97. Question
A 32-year-old woman with a history of major
depressive disorder is found lying on the floor in confusion, with muscles
twitching, flushing, and dilated pupils. On arrival to the emergency
department she is found to have a widened QRS complex. On which of the
following medications did she most likely overdose?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 98 of 198
98. Question
A 29-year-old woman is referred to a
psychiatrist by a primary care physician. The physician informs the
psychiatrist that he believes the patient is exhibiting a somatization
disorder. Which of the following behaviors and symptoms will the
psychiatrist note if this is the correct diagnosis?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 99 of 198
99. Question
A 37-year-old man presents to the emergency
department complaining of swelling of his legs, hands, and face for 4 days.
On examination he is afebrile with generalized edema of his upper and lower
extremities as well as his face. His examination is otherwise notable only
for scars in a linear pattern on his middle to lower arms bilaterally. Basic
metabolic panel and complete blood cell count are normal, but liver function
tests show a total protein level of 5.4 mg/dL and albumin of 2.8 mg/dL.
Urinalysis shows 3+ protein without significant WBCs or RBCs. Which of the
following is the most likely etiology of this patient’s
disease?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 100 of 198
100. Question
A 48-year-old man is brought to the emergency
department confused and disoriented. He re ports recent onset of nausea and
has had several episodes of emesis in the past 4 days. On further
questioning he also notes a metallic taste in his mouth, frequent hiccups,
and pruritus. On physical examination there is a rough, Velcro like sound
heard across his precordium. Which of the following is the most likely
diagnosis?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 101 of 198
101. Question
A 78-year-old man is admitted to the medical
intensive care unit with aspiration pneumonia and sepsis. Before admission,
he had been treated at his nursing home with sulfamethoxazole/ trimethoprim
for a urinary tract infection. In the hospital he is treated with additional
antibiotics for pneumonia and large volumes of fluid. He becomes
hemodynamically stable with treatment, but his fever persists, and he
develops a maculopapular rash on his chest, abdomen, and thighs. His WBC
count is 12,000/mm³ (66% neutrophils, 23% lymphocytes, and 9% eosinophils),
BUN is 34 mg/dL, and creatinine is 2.1 mg/dL. Cultures are negative. Which
of the following is the most likely diagnosis?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 102 of 198
102. Question
56-year-old man presents to the emergency
department because of severe pain in his right ankle. The pain began 4 days
ago, and he denies any history of trauma. His only medical problem is recent
diagnosis of hypertension, for which he takes a mild antihypertensive. His
temperature is 37.2°C (98.9°F), blood pressure is 138/68 mm Hg, pulse is
80/min, and respiratory rate is 14/min. On examination his ankle is swollen,
red, and diffusely tender. Joint fluid aspirate reveals needle-shaped
negatively birefringent crystals under polarized light microscopy. What
medication most likely contributed to his current
presentation?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 103 of 198
103. Question
A 23-year-old woman was recently diagnosed
with systemic lupus erythematosus. At the time of diagnosis she had an
elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate and markedly elevated anti
double-stranded DNA titers. At her rheumatologist’s office, it is discovered
that she has traces of blood in her urine and proteinuria. Renal biopsy is
scheduled, and she is started on a 2-month course of prednisone. Over the
course of her therapy, which drug-related adverse effect is this patient
most likely to experience?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 104 of 198
104. Question
A 65-year-old patient with a history of
bipolar disorder, well-controlled with lithium, is being evaluated for
hypernatremia. Her only com plaint is 4 months of polyuria and thirst. Her
blood pressure is 106/68 mm Hg and pulse is 102/min. Physical examination
reveals her mucous membranes are dry, and skin turgor is normal. The
remainder of the physical examination is unremarkable. Laboratory tests
show: K+ Na+: 147 mEq/L : 4.7 mEq/L Cl−: 110 mEq/L HCO3 −: 24 mEq/L BUN: 12
mg/dL Creatinine: 1.1 mg/dL Plasma osmolality: 305 mOsm/kg Urine osmolality:
200 mOsm/kg. Which of the following is most likely to resolve this patient’s
electrolyte imbalance?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 105 of 198
105. Question
A 52-year-old man is recovering in the
surgical intensive care unit from a total colectomy for colorectal
adenocarcinoma 1 day earlier. He has one peripheral intravenous line that is
being used to run a patient-controlled analgesia pump, 0.5 normal saline at
86 mL/hr, and cefazolin. He has no complaints, appears well, and is
conversational. Relevant laboratory findings are a serum sodium level of 110
mEq/L; his sodium level was 137 mEq/L 1 day earlier. What is the best next
step in the management of this patient?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 106 of 198
106. Question
A 70-year-old woman with a history of renal
artery stenosis presents to the emergency department with decreased urine
output. She was recently started on a new medication by a physician, and a
few days later noticed that she was producing less urine. Otherwise she
feels well and has no complaints. She is afebrile and her blood pressure is
156/88 mm Hg. Laboratory tests show: K+ Na+: 139 mEq/L : 4.1 mEq/L HCO3 −:
24 mEq/L BUN: 41 mg/dL Creatinine: 1.8 mg/dL Urine Na+: 6 mEq/L Urine
creatinine: 11 mg/dL Which of the following medications did she most likely
start recently?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 107 of 198
107. Question
A 65-year-old man with chronic obstructive
pulmonary disease who requires home oxygen at night and has cor pulmonale
presents to the emergency department with worsening shortness of breath. His
respiratory rate is 22/min and heart rate is 104/min. He has distant breath
sounds and is using accessory muscles of breathing. In addition to his
baseline chronic respiratory acidosis, the man is found to have a metabolic
acidosis on arterial blood gas analysis. Laboratory tests show: K+ Na+: 138
mEq/L : 3.6 mEq/L Cl−: 118 mEq/L HCO3 −: 16 mEq/L Phosphate: 2.0 mg/dL
Glucose: 98 mg/dL Blood urea nitrogen (BUN): 10 mg/dL Creatinine: 0.8 mg/dL.
Urinalysis is positive for glucose. Which of the following diagnoses best
explains this patient’s laboratory findings?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 108 of 198
108. Question
A 70-year-old man is investigated for
symptoms of dysphagia. He complains that the symptoms occur only when eating
solids, but not with liquids. There is no pain associated with swallowing
and he reports no weight loss. His physical examination is normal.
Investigations reveal a Zenker diverticulum of the esophagus. Which of the
following historical characteristics suggests a Zenker
diverticulum?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 109 of 198
109. Question
Which of the following conditions would be
best classified as starvation-associated malnutrition?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 110 of 198
110. Question
A 57-year-old man is admitted to the hospital
for dehydration and confusion. In the emergency department he complained of
excessive thirst and he was found to have a serum sodium of 162 meq/L and a
newly elevated creatinine of 2.2 mg/dL. After receiving IV fluid, his
sensorium clears and the patient relays to you that he drinks large amounts
of fluid each day and makes about 2 L of urine each day. He has noticed that
his urine output has no relation to the amount of fluid he drinks. His
sodium remains elevated at 150 meq/L, and his urine osmolality returns at 80
mosmol/kg. After careful water restriction, you administer 10 µg of
desmopressin intranasally and remeasure his urine osmolality. The osmolality
is now 94 mosmol/kg. What is the most likely cause of his
hypernatremia?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 111 of 198
111. Question
You are able to send the patient to the local
hospital to get laboratory values drawn. His serum creatinine is 1.5 mg/dL,
sodium 138 meq/L, potassium 3.8 meq/L, urine creatinine is 12 mmol. Using
the Cockcroft-Gault equation, what is this patient’s creatinine
clearance?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 112 of 198
112. Question
A 52-year-old man is found at home
hypotensive and confused. In the emergency department, his blood pressure is
82/60 mmHg and his heart rate is 115 beats/ min. He is confused and
lethargic. Laboratory data show: Sodium 133 meq/L, potassium 2.4 meq/L,
chloride 70 meq/L, HCO3– 50 meq/L, BUN 44 mg/dL, creatinine 1.7 mg/dL. An
arterial blood gas shows PO2 of 62 mmHg, PCO2 49 mmHg, pH 7.66. What
acid-base disorder is present?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 113 of 198
113. Question
Your clinic patient presents to your office
complaining of numbness and tingling in her hands and around her mouth. On
physical examination, you illicit Chvostek’s sign (twitching of the
circumoral muscles in response to gently tapping on the facial nerve) and
Trousseau’s sign (carpal spasm induced by inflation of a blood pressure cuff
to 20 mmHg above the patient’s systolic blood pressure for 3 min. You make a
presumptive diagnosis of hypocalcemia. What laboratory test is the next step
in diagnosing the cause of her hypocalcemia?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 114 of 198
114. Question
In patients with chronic renal failure, which
of the following is the most important contributor to renal
osteodystrophy?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 115 of 198
115. Question
All the following are complications during
hemodialysis exceptCorrectIncorrect -
Question 116 of 198
116. Question
Preoperative assessment of a 55-year-old male
patient going for coronary angiography shows an estimated glomerular
filtration rate of 33 mL/min per 1.73 m2 and poorly controlled diabetes. He
is currently on no nephrotoxic medications, and the nephrologist assures you
that he does not currently have acute renal failure. The case is due to
begin in 4 h, and you would like to prevent contrast nephropathy. Which
agent will definitely reduce the risk of contrast
nephropathy?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 117 of 198
117. Question
All the following forms of glomerulonephritis
(GN) have associated normal serum complement C4 levels except
….CorrectIncorrect -
Question 118 of 198
118. Question
A 28-year-old woman with HIV on
antiretroviral therapy complains of abdominal pain in the emergency
department. Laboratory data show a creatinine of 3.2 mg/dL; her baseline
creatinine is 1.0 mg/dL. Urinalysis shows large numbers of white blood cells
and red blood cells without epithelial cells, leukocyte esterase, or
nitrites. Which test is indicated to diagnose the cause of her acute renal
failure?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 119 of 198
119. Question
A 79-year-old man has had a diabetic foot
ulcer overlying his third metatarsal head for 3 months but has not been
compliant with his physician’s request to off load the affected foot. He
presents with dull, throbbing foot pain and subjective fevers. Examination
reveals a putrid-smelling wound notable also for a pus-filled 2.5 cm wide
ulcer. A metal probe is used to probe the wound and it detects bone as well
as a 3-cm deep cavity. Gram stain of the pus shows gram-positive cocci in
chains, gram-positive rods, gram-negative diplococci, enteric-appearing
gram-negative rods, tiny pleomorphic gram-negative rods, and a predominance
of neutrophils. Which of the following empirical antibiotic regimens is
recommended while blood and drainage cultures are processed?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 120 of 198
120. Question
A 49-year-old quarry worker undergoes her
yearly employee physical. Screening x-ray of the chest reveals a 1.5-cm
(0.6-in) subpleural parenchymal lesion in the lateral aspect of the right
lung, as well as enlarged hilar nodes, eggshell hilar calcifications, and
multiple small nodules scattered throughout the upper lung fields. The
patient denies cough, weight loss, and night sweats. In fact, she states
that she feels perfectly well. Sputum culture is positive for acid-fast
bacilli. Exposure to which of the following substances increased this
patient’s chance of contracting tuberculosis?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 121 of 198
121. Question
A 38-year-old man with HIV/AIDS presents with
4 weeks of diarrhea, fever, and weight loss.Which of the following tests
makes the diagnosis of cytomegalovirus (CMV) colitis?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 122 of 198
122. Question
In the inpatient setting, extended-spectrum
β-lactamase (ESBL)-producing gramnegative infections are most likely to
occur after frequent use of which of the following classes of
antibiotics?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 123 of 198
123. Question
Sensitive and specific serum or urine
diagnostic tests exist for all of the following invasive fungal infections
except ….CorrectIncorrect -
Question 124 of 198
124. Question
A 78-year-old man has been diagnosed with
mild cognitive impairment after complaining of decreased memory. He asks you
to prescribe something that will decrease his likelihood to progress to
Alzheimer’s disease. Which of the following treatments do you
recommend?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 125 of 198
125. Question
A 48-year-old woman is traveling to Kenya for
a safari. She has no past medical history and is not taking any other
medications. All of the following may be recommended for prophylaxis against
malaria for this patient EXCEPT:CorrectIncorrect -
Question 126 of 198
126. Question
All of the following are minor criteria in
the Modified Duke Criteria for the clinical diagnosis of infective
endocarditis EXCEPT:CorrectIncorrect -
Question 127 of 198
127. Question
Laki-laki 32 tahun dengan riwayat HIV datang
ke RS karena penurunan kesadaran. Pasien juga dilaporkan demam dan sempat
kejang 4 jam yang lalu. Pemeriksaan rangsang meningeal (-). Pada pemeriksaan
CT-scan ditemukan multiple ring enhancing lesion. Apa tatalaksana yang
paling tepat?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 128 of 198
128. Question
Manakah di bawah ini yang bukan pilihan
antibiotik untuk Leptospirosis berat?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 129 of 198
129. Question
A 73-year-old woman has recurrent urinary
tract infections. She is placed on suppressive antibiotic therapy by her
primary physician. One year later, she is complaining of progressive
dyspnea, and a chest radiograph shows development of pulmonary fibrosis.
Which antibiotic could explain development of this
complication?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 130 of 198
130. Question
Manakah di bawah ini yang tidak termasuk
dalam 1-hour bundle sepsis?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 131 of 198
131. Question
A 47-year-old woman with known HIV/AIDS (CD4+
lymphocyte = 106/μL and viral load = 35,000/mL) presents with painful
growths on the side of her tongue as shown in Figure. Which of the following
is the most likely diagnosis?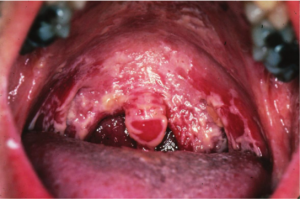 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 132 of 198
132. Question
All of the following are risk factors for the
development of Legionella pneumonia except….CorrectIncorrect -
Question 133 of 198
133. Question
A 38-year-old female pigeon keeper who has no
significant past medical history, is taking no medications, has no
allergies, and is HIV-negative presents to the emergency room with a fever,
headache, and mild nuchal rigidity. Neurologic examination is normal. Head
CT examination is normal. Lumbar puncture is significant for an opening
pressure of 20 cmH2O, white blood cell count of 15 cells/ µL (90%
monocytes), protein of 0.5 g/L (50 mg/mL), glucose of 2.8 mmol/L (50 mg/dL),
and positive India ink stain. What is the appropriate therapy for this
patient?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 134 of 198
134. Question
When given as a first-line agent for invasive
Aspergillus infection, voriconazole commonly causes all of the following
side effects except ….CorrectIncorrect -
Question 135 of 198
135. Question
A 32-year-old man presents with jaundice and
malaise. He is found to have acute hepatitis B with positive hepatitis B
virus (HBV) DNA and E antigen. Which of the following antiviral agents are
approved as part of a therapeutic regimen for monoinfection with hepatitis
B?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 136 of 198
136. Question
Which of the following statements regarding
severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) is true?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 137 of 198
137. Question
Which of the following antibiotics has the
weakest association with the development of Clostridium difficile associated
disease?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 138 of 198
138. Question
Helicobacter pylori colonization is
implicated in all of the following conditions exceptCorrectIncorrect -
Question 139 of 198
139. Question
A previously unvaccinated health care worker
in curs a needle stick from a patient with known active hepatitis B
infection. What is the appropriate management for the health care
worker?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 140 of 198
140. Question
Which of the following is not a common
feature of severe Plasmodium falciparum malaria?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 141 of 198
141. Question
A 26-year-old asthmatic continues to have
coughing fits and dyspnea despite numerous steroid tapers and frequent use
of albuterol over the past few months. Persistent infiltrates are seen on
chest roentgenogram. A pulmonary consultation suggests an evaluation for
allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. What is the diagnostic test of
choice?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 142 of 198
142. Question
A patient who has undergone prosthetic valve
surgery 6 weeks ago is readmitted with signs and symptoms consistent with
infective endocarditis. Which of the following is the most likely etiologic
organism?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 143 of 198
143. Question
You are seeing Mr. DeWinter, a 71-year-old
man, for changes in mental status and cognition. His wife reports that he
has slowly been worsening over the last year or two. He has frequent visual
hallucinations, sleeps heavily during the daytime but not well at night, and
has delusions of persecution. He was noted to have some parkinsonian
features previously and was started on Ldopa, but quickly developed a
hallucinatory delirium requiring cessation of L-dopa. He does not have
orthostatic hypotension or syncope. Which of the following diseases best
fits his dementia syndrome?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 144 of 198
144. Question
A 56-year-old man presents to his physician
complaining of severe fatigue. He began to feel increasingly tired about 6
months ago, but believes that his fatigue has been worsening over the past 3
weeks. He also notes he has had a nonproductive cough for about 2 weeks and
has experienced several episodes of drenching night sweats. On examination
he has several large bruises on his extremities but recalls no injuries.
Abdominal examination reveals massive enlargement of both the liver and the
spleen, without any lymphadenopathy. Laboratory studies show: WBC count:
1200/mm3 Neutrophils: 58% Eosinophils: 7% Lymphocytes: 30% Monocytes: 0%
Basophils: 5% RBC count: 3.0/mm3 Hemoglobin: 7.5 mg/dL Platelet count:
18,000/mm3 Peripheral blood smear reveals irregular nuclei and cell
membranes, as well as cytoplasmic projections. Which of the following is the
most likely diagnosis?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 145 of 198
145. Question
A 47-year-old man presents to his primary
care physician complaining of fatigue for the past several months. He says
he has had poor sleep due to sweating at night and has lost 4.5 kg (10 lb)
recently, although he has not been trying to lose weight. In addition, he
has been suffering from severe headaches and blurry vision recently. On
examination he is pale and thin, with multiple ecchymoses. Cardiac
examination is significant for a II/VI systolic flow murmur. He has an
enlarged spleen on abdominal examination. Laboratory tests show: WBC count:
95,000/mm³, 15% blasts, 15% bands, 47% polymorphonuclear cells, 7%
basophils, 10% lymphocytes, Hemoglobin: 7.2 g/dL Platelet count: 90,000/mm³.
Which of the following is the best next step in establishing a
diagnosis?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 146 of 198
146. Question
Which of the laboratory findings in the table
below are characteristic of hemophilia B?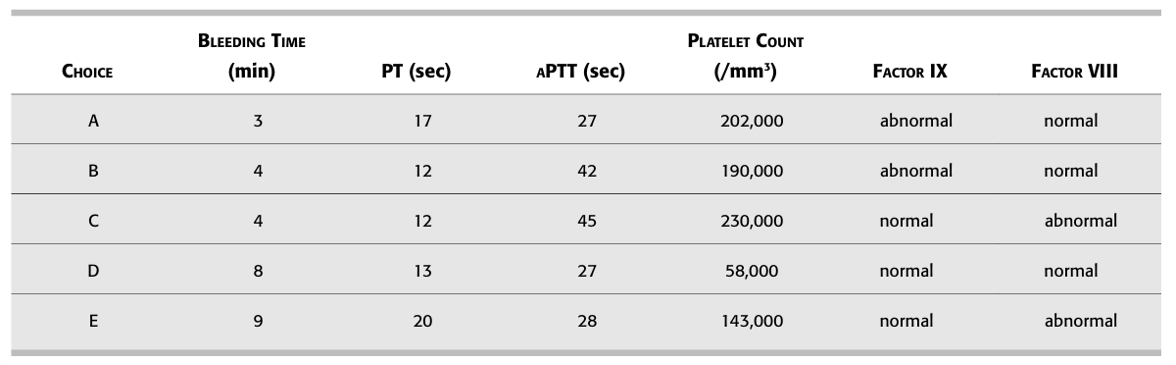 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 147 of 198
147. Question
A 55-year-old woman with a history of
alcoholism and chronic pancreatitis (last exacerbation 2 years ago) presents
to her primary care physician with weight loss, pruritus, anorexia, dark
urine, jaundice, yellow sclera, and vague abdominal pain. Which of the
following physical findings would most strongly support her most likely
diagnosis?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 148 of 198
148. Question
A 68-year-old woman presents to her primary
care physician for a routine visit. She is generally in good health, and her
only medications are hydrochlorothiazide and metoprolol for high blood
pressure. She has had no recent changes in her health, and review of systems
is negative. Examination shows a few enlarged cervical and inguinal lymph
nodes. The liver and spleen are not enlarged. An electrolyte panel is within
normal limits, a peripheral smear shows smudge cells, and a complete blood
cell count shows a WBC count of 47,000/mm³ (with 89% lymphocytes),
hemoglobin level of 12.9 g/dL, and platelet count of 213,000/mm³. Which of
the following is the most appropriate management?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 149 of 198
149. Question
A 30-year-old man presents to his physician
for a routine physical. On questioning he comments that his father was
diagnosed with colon cancer at 45 years of age. The patient has never had
polyps and does not suffer diarrhea, constipation, or bloody stools. The
patient is nervous about screening and wants to delay as long as possible.
According to current recommendations, when should he have his first
colonoscopy?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 150 of 198
150. Question
A 3-year-old patient with sickle cell anemia
is brought to the emergency department complaining of pain in his lower arms
for 3 days. On physical examination both arms are swollen, tender, and
erythematous. He is febrile, and complains of chills. Leukocytosis is seen
on blood count with prominent neutrophils. Which of the following is the
most appropriate treatment?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 151 of 198
151. Question
Which of the laboratory findings in the table
below are characteristic of von Willebrand’s disease?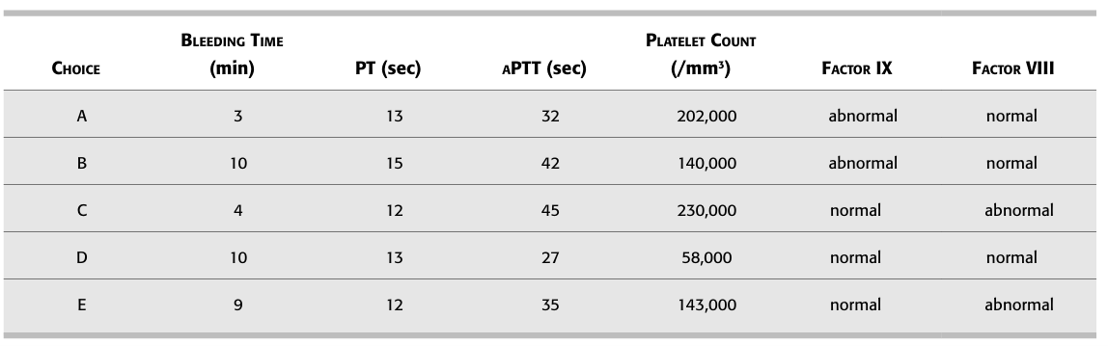 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 152 of 198
152. Question
A 37-year-old woman presents to her physician
with 3 days of fever, fatigue, and rash. Her medications include oral
contraceptives. Her temperature is 38.7°C (101.7°F); she also has a
nonpalpable petechial rash and splenomegaly. Coagulation studies and
fibrinogen levels are normal, but a complete blood cell count shows a
hemoglobin level of 9.7 g/dL and platelet count of 135,000/mm³. A peripheral
blood smear shows schistocytes. Which of the following is the most likely
diagnosis?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 153 of 198
153. Question
A 72-year-old man with a 40-pack-year smoking
history presents with a 9-kg (20-lb) weight loss and fatigue. He has no
other complaints. He is not taking any medication. His physical examination
and vital signs are unremarkable. Laboratory tests show: Na+: 138 mEq/L, K+
: 4.6 mEq/L, Cl−: 101 mEq/L, HCO3 −: 24 mEq/L, Ca2+: 11.2 mg/dL PO4: 1.6
mg/dL, Mg2+: 2.0 mg/dL, Blood urea nitrogen: 11 mg/dL, Creatinine: 1.1
mg/dL, Glucose: 94 mg/dL, Parathyroid hormone: 12 pg/mL Which of the
following is the best next step in the evaluation of this
patient?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 154 of 198
154. Question
A 64-year-old woman with a history of cardiac
disease, multiple strokes, and progressive osteoarthritis is admitted to the
hospital for bilateral total knee replacement surgery. The morning after
surgery her platelet count is 9000/ mm³. Which of the following medications
is most likely responsible for this finding?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 155 of 198
155. Question
A 68-year-old man has been treated for non
Hodgkin’s lymphoma for the past 3 weeks, and now complains of weakness and
fatigue for the past day. His temperature is 38.5°C (101.3°F), blood
pressure is 140/88 mm Hg, and heart rate is 78/min. The remainder of the
examination is normal. Laboratory tests show: K+ Na+: 136 mEq/L : 5.8 mEq/L
Cl−: 99 mEq/L Ca2+: 7.9 mEq/L HCO3 −: 25 mEq/L Blood urea nitrogen: 9 mg/dL
Creatinine: 0.9 mg/dL Urate: 9.1 mg/dL What is the most likely cause of this
patient’s hyperkalemia?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 156 of 198
156. Question
A 67-year-old woman is seen in the doctor’s
of f i ce for a cough productive of bloody sputum and an 11.3-kg (25-lb)
unintentional weight loss, both occurring within the past 6 months. In
addition, the patient notes that over the past 3 months she has become
increasingly lethargic and experienced bouts of nausea. She has smoked two
packs per day for the past 50 years. She denies a history of heart failure
or liver cirrhosis. She currently takes no medications. Her temperature is
36.7°C (98.1°F), blood pressure is 125/85 mm Hg, pulse is 78/min and
regular, respiratory rate is 15/min, and oxygen saturation is 99% on room
air. Examination reveals crackles at the left lower lung field; no lower
extremity edema is present. Laboratory test show: K+ WBC count: 6000/mm3
Hemoglobin: 14.7 g/dL Platelet count: 210,000/mm3 Na+: 125 mEq/L : 4 mEq/L
Cl−: 102 mEq/L CO2: 24 mmol/L Blood urea nitrogen: 8 mg/dL Creatinine: 1
mg/dL Glucose: 120 mg/dL Urine osmolality: 125 mOsm/kg Urinary Na+: 35 mEq/L
X-ray of the chest shows a focal 5-cm mass lesion in the right lower lung
that is corroborated by CT. Which of the following is the most likely
histologic type of lung cancer present in this patient?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 157 of 198
157. Question
A 59-year-old man presents to the clinic with
a 6.8-kg (15-lb) weight loss over 2 months, with occasional night sweats. He
notices some abdominal fullness but no pain, and his last colonoscopy was
negative for polyps. He has never smoked tobacco, but he has had prior
radiation exposure as an x-ray technician. Physical examination is
significant for splenomegaly, with no signs of jaundice. Fecal occult blood
is negative. X-ray of the chest is clear. His WBC count is 126,000/mm³, and
a peripheral smear shows a leukocytosis with all stages of maturation seen
and 3% blasts. Which of the following tests would confirm the
diagnosis?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 158 of 198
158. Question
A 32-year-old woman presents to the emergency
department with edema and pain of the right lower extremity that began after
a 6-hour car ride. A Doppler ultrasound was completed in which a deep vein
thrombosis (DVT) was noted. The patient has no prior history of DVT or
pulmonary emboli. The patient has been taking oral contraceptive pills for
the past 2 years and is currently compliant with her medication. Her family
history is significant for a maternal grandmother, mother, and sister with
recurrent DVT. Her temperature is 36.2°C (97.2°F), blood pressure is 112/78
mm Hg, heart rate is 86/min, and respiratory rate is 14/ min. There is no
clinical evidence indicating a pulmonary embolism. Which of the following is
the most likely cause of her DVT?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 159 of 198
159. Question
A 50-year-old female presents to your clinic
for evaluation of an elevated platelet count. The latest complete blood
count is white blood cells (WBC) 7,000/mm3, hematocrit 34%, and platelets
600,000/mm3. All the following are common causes of thrombocytosis
exceptCorrectIncorrect -
Question 160 of 198
160. Question
All the following are suggestive of iron
deficiency anemia except ….CorrectIncorrect -
Question 161 of 198
161. Question
You are seeing a patient in follow-up in whom
you have begun an evaluation for an elevated hematocrit. You suspect
polycythemia vera based on a history of aquagenic pruritus and splenomegaly.
Which set of laboratory tests are consistent with the diagnosis of
polycythemia vera?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 162 of 198
162. Question
All the following are characteristic of tumor
lysis syndrome exceptCorrectIncorrect -
Question 163 of 198
163. Question
All of the following laboratory values are
consistent with an intravascular hemolytic anemia exceptCorrectIncorrect -
Question 164 of 198
164. Question
A 48-year-old male has a long-standing
history of ankylosing spondylitis. His most recent spinal film shows
straightening of the lumbar spine, loss of lordosis, and “squaring” of the
vertebral bodies. He currently is limited by pain with ambulation that is
not improved with non steroidal anti-inflammatory medications. Which of the
following treatments has been shown to improve symptoms the best at this
stage of the illness?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 165 of 198
165. Question
Which of the following findings on joint
aspiration is most likely to be associated with calcium pyrophos phate
deposition disease (pseudogout)?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 166 of 198
166. Question
Seorang laki laki usia 68 tahun seorang
perokok berat datang ke IGD dengan keluhan sesak. Pasien memiliki riwayat
PPOK sejak 10 tahun. Dokter IGD memberikan pasien obat golongan SABA, LAMA
dan glukokortikoid dosis tinggi. Jika pasien dilakukan pemeriksaan EKG,
manakah perubahan EKG dibawah ini yang merupakan akibat pemberian obat
glukokortikoid di IGD?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 167 of 198
167. Question
A 46-year-old woman is referred to your
clinic by her primary care physician. She describes fatigue and diffuse
muscle aches that have been worsening over a period of 6 months. She also
has not been sleeping well. Her primary doctor evaluated her and sent
screening laboratory tests, which returned with a positive rheumatoid
factor. She has read about rheumatoid arthritis on the Internet and is very
concerned that she has the disease based on her symptoms and her positive
test. Which of the following is true in regard to diagnosing rheumatoid
arthritis (RA)?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 168 of 198
168. Question
A 46-year-old woman presents to your clinic
with multiple complaints. She describes fatigue and general malaise over 2–3
months. Her appetite has decreased. She thinks she has unintentionally lost
~5.5 kg. Lately she notes pain and stiffness in her fingers on both hands
that is worse in the morning and with repetitive movement. She has a
grandmother and a sister who have rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and she is very
concerned that she now has it as well. Which of her complaints represents
the most common manifestation of established RA?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 169 of 198
169. Question
A 62-year-old female complains of aching
joints. She notes intermittent stiffness and pain in the knees, hips,
wrists, and hands. She also describes easy fatigability, dyspepsia, a dry
cough, and itchy red eyes and also has trouble keeping her dentures in
place. There is a history of diabetes but no other significant history.
Medications include insulin and naproxen. She has no HIV risk factors.
Examination is significant for dry mucous membranes in the oropharynx. There
is no evidence of joint destruction or active inflammation. Laboratory
studies show a negative antinucleolar antibody but a positive Ro/ SSA
autoantigen. What is the most likely diagnosis?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 170 of 198
170. Question
A 53-year-old woman presents to your clinic
complaining of fatigue and generalized pain that have worsened over 2 years.
She also describes irritability and poor sleep and is concerned that she is
depressed. She reveals that she was recently separated from her husband and
has been stressed at work. Which of the following elements of her
presentation meet American College of Rheumatology criteria for
fibromyalgia?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 171 of 198
171. Question
A 43-year-old man presents to your clinic
complain ing of bilateral knee pain. He states that the pain worsens with
walking and is not present at rest. He has been expe riencing knee pain for
many months and has had no relief from over-thecounter analgesics. He has a
history of hy pertension and obesity. Which of the following represents the
best initial treatment strategy for this patient?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 172 of 198
172. Question
A 45-year-old African-American woman with sys
temic lupus erythematosus (SLE) presents to the emer gency room with
complaints of headache and fatigue. Her prior manifestations of SLE have
been arthralgias, hemolytic anemia, malar rash, and mouth ulcers, and she is
known to have high titers of antibodies to double stranded DNA. She
currently is taking prednisone, 5 mg daily, and hydroxychloroquine, 200 mg
daily. On presen tation, she is found to have a blood pressure of 190/110
mmHg with a heart rate of 98 beats/min. A urinalysis shows 25 red blood
cells (RBCs) per high-power field with 2+ proteinuria. No RBC casts are
identified. Her blood urea nitrogen is 88 mg/dL, and creatinine is 2.6 mg/dL
(baseline 0.8 mg/dL). She has not previously had renal disease related to
SLE and is not taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. She denies any
recent illness, decreased oral intake, or diarrhea. What is the most ap
propriate next step in the management of this patient?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 173 of 198
173. Question
A 23-year-old woman was diagnosed with
systemic lupus erythematosus based upon the presence of polyar thritis,
malar rash with photosensitivity, and oral ulcer ations. Antibodies to
double-stranded DNA, Smith protein, and antinuclear antibodies were present
in high titers. A urinalysis is normal. The patient is requesting treatment
for the joint symptoms as she feels they limit her activities of daily
living. What is the best choice for initial therapy in this
individual?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 174 of 198
174. Question
A 45-year-old male has been hospitalized for
several weeks in the intensive care unit for postsurgical compli cations
after gastrojejunal bypass surgery. He is noted to have persistent fevers
and on examination is found to have erythema, fluctuance, and tenderness
over the pos terior surface of the left elbow. Initial management of this
disorder should include all the following except ….CorrectIncorrect -
Question 175 of 198
175. Question
What is the most common extraarticular
manifestation of ankylosing spondylitis?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 176 of 198
176. Question
A 58-year-old female presents complaining of
right shoulder pain. She does not recall any prior injury but notes that she
feels that the shoulder has been getting progressively more stiff over the
last several months. She previously had several episodes of bursitis of the
right shoulder that were treated successfully with NSAIDs and steroid
injections. The patient’s past medical history is also significant for
diabetes mellitus, for which she takes metformin and glyburide. On physical
examination, the right shoulder is not warm or red but is tender to touch.
Passive and active range of motion is limited in flexion, extension, and
abduction. A right shoulder radiogram shows osteopenia without evidence of
joint erosion or osteophytes. What is the most likely
diagnosis?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 177 of 198
177. Question
A 31-year-old woman presents to your clinic
complaining of painful arthritis that is worse in the mornings when she
wakes up. She was recently evaluated by an ophthalmologist for uveitis in
her right eye. A recent laboratory report shows an erythrocyte sedimentation
rate of 48 mm/h. Which of the following will be helpful in distinguishing
relapsing polychondritis from rheumatoid arthritis (RA)?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 178 of 198
178. Question
A 54-year-old female with rheumatoid
arthritis is treated with infliximab for refractory disease. All the
following are potential side effects of this treatment
exceptCorrectIncorrect -
Question 179 of 198
179. Question
Which of the following joints are typically
spared in osteoarthritis (OA)?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 180 of 198
180. Question
Which of the following definitions best fits
the term enthesitis?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 181 of 198
181. Question
Seorang perempuan usia 53 tahun dengan
riwayat diabetes mellitus tipe 2 datang ke klinik mengeluhkan lelah dan
tidak enak badan di pagi hari. Pasien rutin melakukan cek gula darah mandiri
dan mengaku sering mendapati gula darahnnya sekitar 120 saat malan dan
meningkat menjadi 170 -180 saat pagi hari. Pasien sudah mencoba untuk
mengurangi asupan karbohidrat saat malam namun justru sedikit memburuk.
Manakah dibawah ini yang dapat meringankan kondisi pasien?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 182 of 198
182. Question
A 42-year-old man presents to your clinic
complain ing of left shoulder soreness that has been bothering him for 8
months. He experiences intermittent pain that is worse at night. Active
abduction of his left arm over his head causes extreme pain. He describes
his pain as a dull ache in his shoulder. He cannot identify a specific
trauma that led to his pain but notes that he lifts weights and plays sports
on a regular basis. On physical examination, he has tenderness over the
lateral aspect of the humeral head and pain with arm abduction. Which of the
follow ing is the most likely cause of his symptoms?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 183 of 198
183. Question
All the following organisms have been
implicated in reactive arthritis except ….CorrectIncorrect -
Question 184 of 198
184. Question
A 45-year-old male comes to your office for
evaluation of chest pain. He reports substernal chest pressure, lasts a few
minutes, does not radiate to his shoulder or jaw, occurs with exertion
sometimes, and is relieved on its own in a few minutes. His risk factors
include hypertension controlled on hydrachlorothiazide and amlodipine. He
also was a 20 pack a year smoker, but quit a month ago. His
electrocardiogram (ECG) shows no abnormalities. To evaluate his chest pain,
what should the next step be?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 185 of 198
185. Question
A 75-year-old man with hypertension is on
lisinopril 40 mg/day and HCTZ 50 mg/day. His BP is 160/88 mmHg. Previously,
he did not tolerate diltiazem because of edema. What would you
do?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 186 of 198
186. Question
What is the correct interpretation of this
electrocardiogram (ECG) tracing?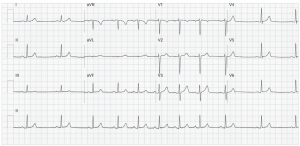 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 187 of 198
187. Question
A 54-year-old male is brought to the
emergency de partment with 1 hour of substernal crushing chest pain, nausea,
and vomiting. He developed the pain while playing squash. The pain was
improved with the administration of sublingual nitroglycerine in the field.
His ECG is shown below. Emergent cardiac catheterization is most likely to
show acute thrombus in which of the following vessels?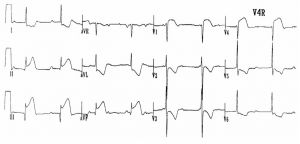 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 188 of 198
188. Question
A 62-year-old female with a history of
chronic left bundle branch block is admitted to the coronary care unit with
4 hours of substernal chest pain and shortness of breath. She has elevation
of serum troponin-T. She receives urgent catheterization with angioplasty
and stent place ment of a left anterior descending (LAD) artery lesion.
Three days after admission she develops recurrent chest pain. Which of the
following studies is most useful for detecting new myocardial damage since
the initial infarction?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 189 of 198
189. Question
Acute hyperkalemia is associated with which
of the following electrocardiographic changes?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 190 of 198
190. Question
Based on the electrocardiogram below,
treating which condition might specifically improve this patient’s
tachycardia?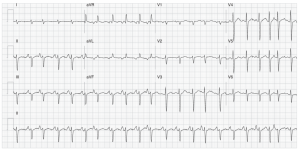 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 191 of 198
191. Question
A 72-year-old man seeks evaluation for leg
pain with ambulation. He describes the pain as an aching to crampy pain in
the muscles of his thighs. The pain subsides within minutes of resting. On
rare occasions, he has noted numb ness of his right foot at rest and pain in
his right leg has woken him at night. He has a history of hypertension and
cerebrovascular disease. He previously had a transient is chemic attack and
underwent right carotid endarterectomy 4 years previously. He currently
takes aspirin, irbesartan, hydrochlorothiazide, and atenolol on a daily
basis. On ex amination, he is noted to have diminished dorsalis pedis and
posterior tibial pulses bilaterally. The right dorsal pedis pulse is faint.
There is loss of hair in the distal extremities. Capillary refill is
approximately 5 s in the right foot and 3 s in the left foot. Which of the
following findings would be suggestive of critical ischemia of the right
foot?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 192 of 198
192. Question
A 25-year-old man presents to the clinic with
complaints of pain in his feet with walking. He reports this has been going
on for several months and has progressively worsened in the past few weeks.
He is beginning to develop symptoms in his right calf and earlier this week
noticed a black area on his great toe. He has no medical problems, takes no
medications, and is in good health overall. He is a smoker and works as a
computer salesman. He reports a family history of VTE; his mother had a
pulmonary embolism at the age of 50 and was diagnosed with the
antiphospholipid antibody syndrome. What is the most likely cause of his
symptoms?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 193 of 198
193. Question
A 55-year-old woman presents to the ED with
precordial chest discomfort and shortness of breath. Her body mass index is
34. Her medical history includes essential hypertension, diabetes mellitus
type 2, and a 30 pack-year smoking history. Laboratory results include a
troponin of 2.4 mg/mL and a B-type natriuretic peptide of 840 pg/mL. An ECG
reveals no ST-segment elevation and nonspecific ST-T wave changes. The ED
physician requests cardiology consultation for an NSTEMI. When you arrive to
see the patient you order an IV contrast-enhanced chest CT scan of the
lungs. Findings are demonstrated in figure below. What is the
diagnosis?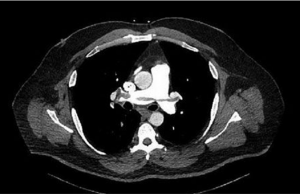 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 194 of 198
194. Question
A 35-year-old man is evaluated for dyspnea.
He first noticed shortness of breath with exertion about 12 months ago. It
has become progressively worse such that he is only able to walk about 20 ft
without stopping. In general, he rates his health as good, although he
recalls being told when he was younger that he had a heart mur mur. He has
not seen a physician in 15 years. On exami nation, he is noted to be hypoxic
with an SaO2 of 85% on room air. His cardiac examination reveals a harsh ma
chinery-like murmur that is continuous throughout sys tole and diastole with
a palpable thrill. There is late systolic accentuation of the murmur at the
upper left ster nal angle. He is noted to have cyanosis and clubbing of his
toes but not his fingers. What is the most likely cause of the patient’s
murmur?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 195 of 198
195. Question
Which of the following congenital heart
defects causes fixed splitting of the second heart sound?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 196 of 198
196. Question
A 68-year-old man with a history of
myocardial in farction and congestive heart failure is comfortable at rest.
However, when walking to his car, he develops dyspnea, fatigue, and
sometimes palpitations. He must rest for several minutes before these
symptoms resolve. His New York Heart Association classification is which of
the following?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 197 of 198
197. Question
A 63-year-old man with non-insulin-dependent
diabetes mellitus, HTN, hyperlipidemia, and chronic renal insufficiency is
admitted with acute anterior wall MI 10 hours after symptom onset. He is
taken emergently to the cardiac catheterization laboratory. He is noted to
have proximal LAD occlusion, and he undergoes a successful PTCA/stent to the
LAD with abciximab and heparin. His EF is noted to be 30% on a TTE performed
3 days later. On hospital day 4, he reports chest pain and is found to be in
AFib with an HR of 121. His BP is 90/44 mmHg, and he is short of breath and
anxious. Which of the following should you administer next?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 198 of 198
198. Question
A 45-year-old man is admitted to the
intensive care unit with symptoms of congestive heart failure. He is
addicted to heroin and cocaine and uses both drugs daily via injection. His
blood cultures have yielded methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus in
four of four bottles within 12 h. His vital signs show a blood pressure of
110/40 mmHg and a heart rate of 132 beats/min. There is a IV/VI diastolic
murmur heard along the left sternal border. A schematic representation of
the carotid pulsation is shown in the figure below. What is the most likely
cause of the patient’s murmur?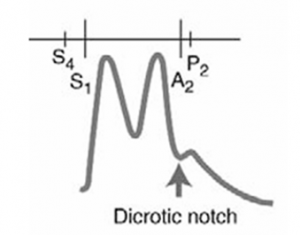 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect
